AKAP Accreditation Organization

$380.00 – $430.00Price range: $380.00 through $430.00
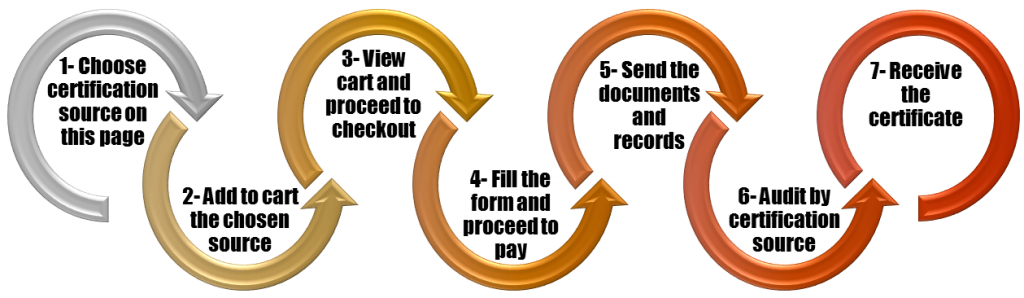
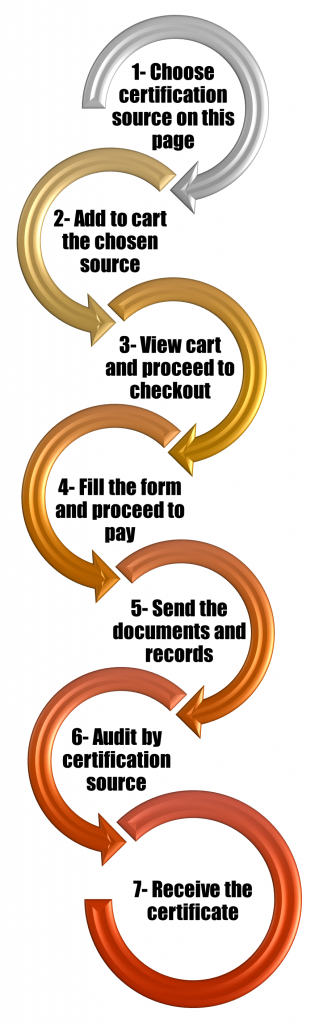
Further details
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) As a core foundation of health and safety systems contains a set of requirements and guidelines that describe the methods, equipment, facilities and controls required to produce high quality products in the following aspects:
-Medicinal products for humans and veterinary uses
-Biological products
-Products made from natural sources such as humans, animals or microorganisms
-Medical Equipment
-Processed Foods
The purpose of formulating these criteria is to guide manufacturers to establish minimum good production conditions, to maintain them and to produce high quality products, and to ensure that products are manufactured and controlled in accordance with the standards appropriate to their usage, and meet consumer needs in terms of quality, safety and efficiency. Having a good construction certificate indicates that the certificate holder respects the provisions contained therein and thus assures the consumer of its quality.
The principles of GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) are control factors that focus on the whole production and quality control operation rather than on a specific process. GMP is the pillar of a healthy product that creates and maintains suitable infrastructure for production including machinery, environment, equipment, manpower, and so on.
In summary, the main requirements of the GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) Rules of Procedure are as follows:
Define all production processes clearly, systematically, operationally, and revised, so that the product’s capacity and ability to produce the product have been proven to be of the highest quality and in accordance with the predicted specifications.
Validation of key and sensitive steps of production processes and major changes in each process.
Provide the following facilities and supplies:
-Appropriate, skilled and trained personnel
-Adequate building and space
-Appropriate equipment and services
-The correct materials, containers and labels
-Convenient storage and transportation
-Approved guidelines and disciplines
-Formulating guidelines and disciplines, especially for the use of tools and facilities, clearly, operationally, in a simple, unambiguous language.
Training operators so that they are prepared to perform the processes correctly.
Preparation of manual / machine records during production operations, in a manner that reflects all steps and requirements in accordance with defined guidelines and disciplines and Production of product with quantitative and qualitative specifications is anticipated.
Any risk deviation should be recorded and examined.
Maintain records and papers of various stages of production, including complete and traceable records of comprehensive and accessible distribution of products with minimal bugs in quality.
Existence of an available system to recover bulk and partially sold products
Having a system for investigating complaints about sold products, investigating the cause of quality defects, correcting and preventing repetition.
Good manufacturing practices (GMP) are the practices required in order to conform to the guidelines recommended by agencies that control the authorization and licensing of the manufacture and sale of food and beverages, cosmetics, pharmaceutical products, dietary supplements, and medical devices. These guidelines provide minimum requirements that a manufacturer must meet to assure that their products are consistently high in quality, from batch to batch, for their intended use. The rules that govern each industry may differ significantly; however, the main purpose of GMP is always to prevent harm from occurring to the end user.
Additional tenets include ensuring the end product is free from contamination, that it is consistent in its manufacture, that its manufacture has been well documented, that personnel are well trained, and that the product has been checked for quality more than just at the end phase. GMP is typically ensured through the effective use of a quality management system (QMS).
Good manufacturing practices, along with good agricultural practices, good laboratory practices and good clinical practices, are overseen by regulatory agencies in the United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Europe, China, India and other countries.

Benefits of ISO implementation:
– Increase customer and consumer confidence
– Increasing the quality of products/services
– Reduce waste and losses in products/services and ultimately reduce costs
– Save on consumables and increase profits
– Planning, implementation of affairs in the form of a predefined international system
– Improve performance, increase productivity and speed in affairs
– Increase efficiency and customer satisfaction
– Reducing the number of complaints
– Improvement and uniformity in the quality of products/services
– Timely delivery of products/services
– Global competition
– Prevent or reduce unexpected events
– Earning points in tenders, obtaining ranks and grades from government organizations, providing evidence in exports
Other benefits are:
– Advertising use in headers, company site and all advertising matters
– Earn points in selecting sample units
– Reduce waste and waste time
– Creating confidence inside and outside the organization
– Transparency of processes and indicators
– Ensuring that customer needs and expectations are met
– Production of product/service with better quality
– Help with more marketing and sales and create demand
– Increasing the productivity and motivation of human resources
– Correcting errors and preventing their recurrence
– Improving communication within the organization
– Prevention of non-compliant product/service production
– Develop sales methods and provide after-sales service
$420.00 – $460.00Price range: $420.00 through $460.00
$380.00 – $420.00Price range: $380.00 through $420.00
$500.00 – $530.00Price range: $500.00 through $530.00
$320.00 – $350.00Price range: $320.00 through $350.00
$380.00 – $420.00Price range: $380.00 through $420.00