AKAP Accreditation Organization

$360.00 – $380.00Price range: $360.00 through $380.00
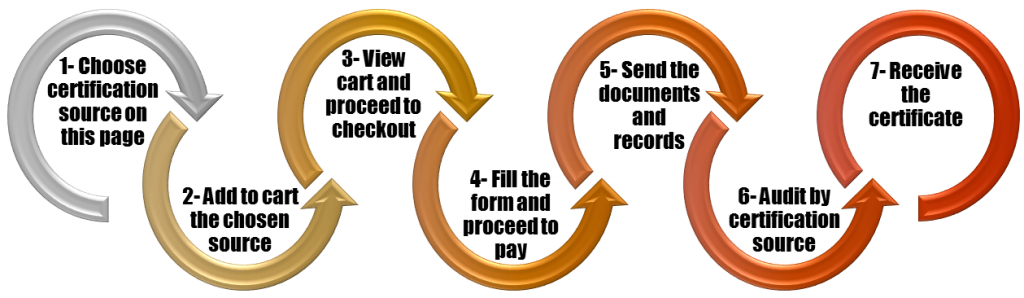
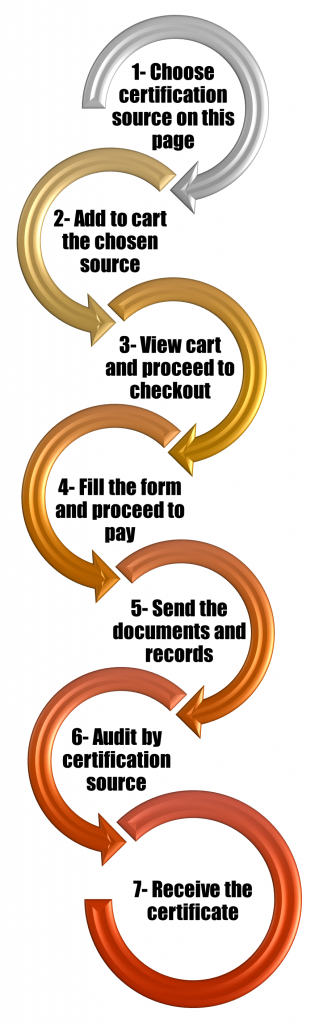
Further details
HSE-MS means Health, safety and Environment Management System.
s a methodology that studies and implements practical aspects of protection of environment, health and safety at occupation. In simple terms it is what organizations must do to make sure that their activities do not cause harm to anyone. Commonly, quality – quality assurance & quality control – is adjoined to form the company division known as HSQE.
From a safety standpoint, it involves creating organized efforts and procedures for identifying workplace hazards and reducing accidents and exposure to harmful situations and substances. It also includes training of personnel in accident prevention, accident response, emergency preparedness, and use of protective clothing and equipment.
Better health at its heart, should have the development of safe, high quality, and environmentally friendly processes, working practices and systemic activities that prevent or reduce the risk of harm to people in general, operators, or patients.
From an environmental standpoint, it involves creating a systematic approach to complying with environmental regulations, such as managing waste or air emissions all the way to helping site’s reduce the company’s carbon footprint.
Regulatory requirements play an important role in EHS discipline and EHS managers must identify and understand relevant EHS regulations, the implications of which must be communicated to executive management so the company can implement suitable measures.
The HSE-MS is the basis of both ISO 14001 Environmental Management System and ISO 45001 Occupational Health and Safety Assessment Series. If two sets of standards are to be designed and implemented in each set, it is said to have implemented the HSE suite. Due to the inclination of collections to implement two standards, a model was created to combine these two standards. Therefore, the combination of the two ISO 14001 and ISO 45001 standards was called the HSE or HSE MS model.
HSE Risk Management Hierarchy:
Elimination:
Risk elimination is the complete elimination of risk. Completely eliminating a risk is often not possible but once the risk is completely eliminated it will have a significant impact on the productivity of the company / organization.
Replace:
Replacement is done when the risk components of the system are replaced with the low risk type.
Isolation:
Isolation involves placing the hazard at a location farther away or confined to other operating segments and individuals.
Engineering Controls:
Such as PM system or maintenance and other engineering control measures.
Administrative Act Controls:
Includes inspections, visits, policies, procedures, operating instructions, training, and incentive mechanisms (reward and punishment).
Personal Protection Equipment (PPE):
Using PPE is the latest way to control the risks that people are exposed to.
The HSE (Health, safety and Environment ) Plan is a document that all units are required to operate on a continuous basis while doing the work.The HSE Plan is a vibrant, dynamic document that must be reviewed throughout the duration of the safety, health and environmental plan.
Therefore, the system used to execute the above program is based on the effective and highly applicable Deming Management Cycle to achieve the goal of continuous improvement. The main steps in this Deming Management System are as follows:
-Plan
-Do
-Check
-Action
In this step-by-step management system, Plan means the basic planning of the plans to maintain and improve the HSE system level, DO means implementing all the plans presented in the plan stage, The Check step is the basic step to get feedback from the executed system and to find the mismatches in the system Finally, Action is to address the relevant mismatches in each of the individual HSE segments and to continuously improve the safety, health, and environment system of the industry.

Benefits of ISO implementation:
– Increase customer and consumer confidence
– Increasing the quality of products/services
– Reduce waste and losses in products/services and ultimately reduce costs
– Save on consumables and increase profits
– Planning, implementation of affairs in the form of a predefined international system
– Improve performance, increase productivity and speed in affairs
– Increase efficiency and customer satisfaction
– Reducing the number of complaints
– Improvement and uniformity in the quality of products/services
– Timely delivery of products/services
– Global competition
– Prevent or reduce unexpected events
– Earning points in tenders, obtaining ranks and grades from government organizations, providing evidence in exports
Other benefits are:
– Advertising use in headers, company site and all advertising matters
– Earn points in selecting sample units
– Reduce waste and waste time
– Creating confidence inside and outside the organization
– Transparency of processes and indicators
– Ensuring that customer needs and expectations are met
– Production of product/service with better quality
– Help with more marketing and sales and create demand
– Increasing the productivity and motivation of human resources
– Correcting errors and preventing their recurrence
– Improving communication within the organization
– Prevention of non-compliant product/service production
– Develop sales methods and provide after-sales service
$420.00 – $480.00Price range: $420.00 through $480.00
$380.00 – $420.00Price range: $380.00 through $420.00
$390.00 – $430.00Price range: $390.00 through $430.00
$400.00 – $450.00Price range: $400.00 through $450.00
$330.00 – $360.00Price range: $330.00 through $360.00