AKAP Accreditation Organization

$370.00 – $400.00Price range: $370.00 through $400.00
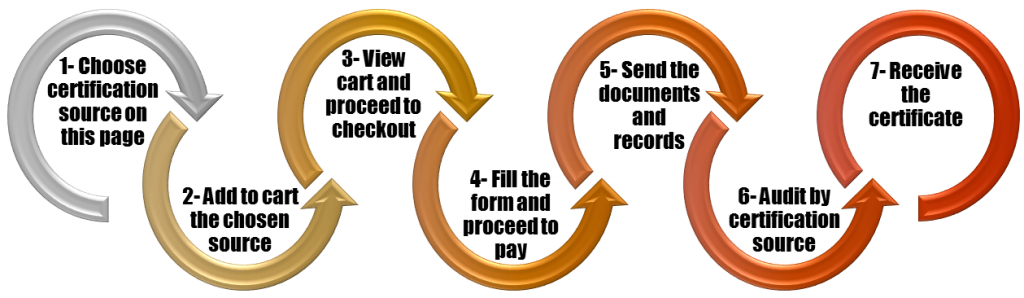
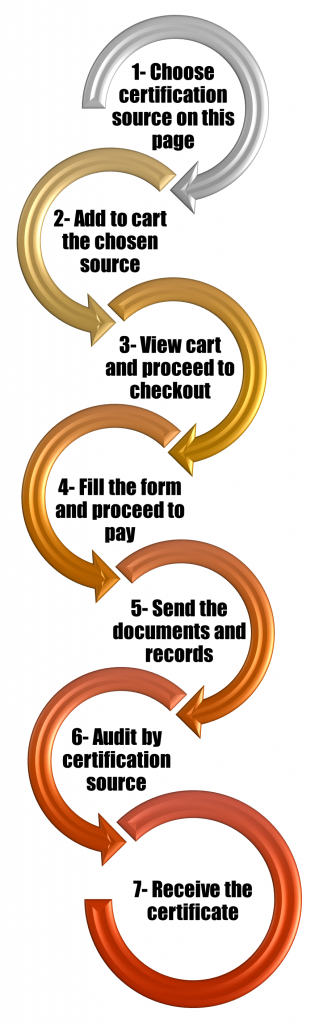
Further details
The GLP (good laboratory practice) standard is a global rule and standard for managing how a product works and is produced in a laboratory. In this way, in the experimental and non-clinical basin, it is possible to ensure the accuracy of coordination, stability, validity, reproducibility, quality and correctness of chemical product production, which also includes pharmaceutical products in the laboratory environment.
The GLP (good laboratory practice) system is actually related to controlling the quality of performance in laboratory environments and uses personnel (human resources), laboratory environment, how to collect relevant documents, how it works, the equipment used, the raw materials used And generally includes all steps of production. It should be noted that international education is also needed for the proper implementation of these laws. Today, the Food and Drug Administration of any country that follows this global standard has the authority to control and approve GLP practices and can monitor the construction and operation of laboratories that operate on these principles.
good laboratory practice or GLP is a quality system of management controls for research laboratories and organizations to ensure the uniformity, consistency, reliability, reproducibility, quality, and integrity of products in development for human or animal health (including pharmaceuticals) through non-clinical safety tests; from physio-chemical properties through acute to chronic toxicity tests.
GLP (good laboratory practice) was first introduced in New Zealand and Denmark in 1972, and later in the US in 1978 in response to the Industrial BioTest Labs scandal. It was followed a few years later by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Principles of GLP in 1992; the OECD has since helped promulgate GLP to many countries.
GLP (good laboratory practice) applies to non-clinical studies conducted for the assessment of the safety or efficacy of products in development (including pharmaceuticals) for man, animals and the environment. GLP, a data and operational quality system, is not the same as standards for laboratory safety – appropriate gloves, glasses and clothing to handle lab materials safely. The principles of GLP aim to ensure and promote safety, consistency, high quality, and reliability of chemicals in the process of non-clinical and laboratory testing. GLP is not limited to chemicals and also applies to medical devices, food additives, food packaging, colour additives, animal food additives, other non-pharmaceutical products or ingredients, biological products, and electronic products.
One of the principles that is considered in this standard is the effect of chemicals on humans, animals and the environment. GLPs are also rules based on quality systems and should not be confused with other standards that focus on proper safety, such as glasses, gloves, and employee clothing, which is to maintain the safety of the laboratory.
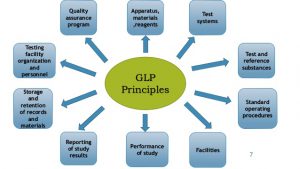
Benefits of ISO implementation:
– Increase customer and consumer confidence
– Increasing the quality of products/services
– Reduce waste and losses in products/services and ultimately reduce costs
– Save on consumables and increase profits
– Planning, implementation of affairs in the form of a predefined international system
– Improve performance, increase productivity and speed in affairs
– Increase efficiency and customer satisfaction
– Reducing the number of complaints
– Improvement and uniformity in the quality of products/services
– Timely delivery of products/services
– Global competition
– Prevent or reduce unexpected events
– Earning points in tenders, obtaining ranks and grades from government organizations, providing evidence in exports
Other benefits are:
– Advertising use in headers, company site and all advertising matters
– Earn points in selecting sample units
– Reduce waste and waste time
– Creating confidence inside and outside the organization
– Transparency of processes and indicators
– Ensuring that customer needs and expectations are met
– Production of product/service with better quality
– Help with more marketing and sales and create demand
– Increasing the productivity and motivation of human resources
– Correcting errors and preventing their recurrence
– Improving communication within the organization
– Prevention of non-compliant product/service production
– Develop sales methods and provide after-sales service
$390.00 – $410.00Price range: $390.00 through $410.00
$410.00 – $440.00Price range: $410.00 through $440.00
$380.00 – $400.00Price range: $380.00 through $400.00
$400.00 – $460.00Price range: $400.00 through $460.00
$450.00 – $500.00Price range: $450.00 through $500.00